In 2020, I, along with my partners at SMP&CO, developed the EduBox, where we used Raspberry Pis to aid students in remote learning. We positioned it as a better-value alternative to the phones, tablets, and paper worksheets being distributed by government agencies at the time.
While I was looking back at the project, I stumbled upon some technical notes regarding the Raspberry Pi's composite video output. The Raspberry Pi's 3.5mm port outputs not only audio but video as well. However, this feature came with a caveat.
The Raspberry Pi uses an uncommon pole layout, as illustrated below:
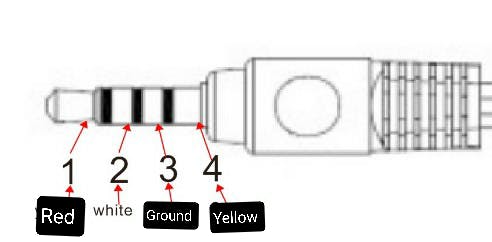
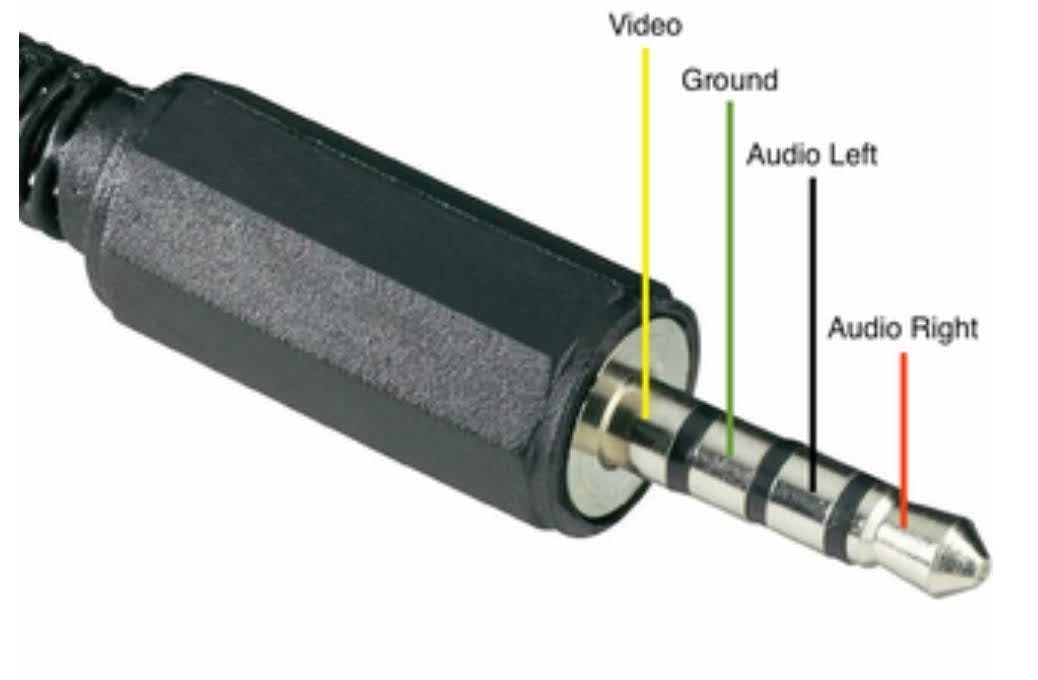
I believe this layout is the same one used on select models of the iPod.
This layout is quite uncommon, given that the iPod dropped support for composite video out via the 3.5mm jack all the way back in 2007. When I was trying to source cables with the correct pole layout, almost all the suppliers I inquired with on Alibaba needed to create a special production line, thus increasing the minimum order quantity to volumes we cannot commit to. Many flat-out refused.
We wanted to bundle a composite cable with our EduBox so that households with older TVs could use the EduBox. One of the biggest drawbacks of the EduBox concept was that it did not include a screen — so instead, to keep costs down, we opted to use the household's existing TVs as the screen. Given that we were aiming to distribute EduBoxes to low-income households, it was important that the EduBox was compatible with older TVs that only had composite video input.


